Solar Photovoltaic
Electrical Properties of PV Modules
Each PV module can be characterized by its performance curve, i.e. the current-voltage curve (I-V curve). The performance of solar module is tested under standard testing conditions (STC) as defined in the IEC 60904 standards: cell temperature of 25 degrees Celsius, incident solar irradiance of 1000 W/m2, spectral distribution of the light spectrum with an air mass AM = 1.5.

Above: I-V characteristics of a PV module
Three points on the I-V curve are important in defining the performance of a PV module, i.e. the maximum power point, the short-circuit current and the open-circuit voltage.
- The maximum power point (MPP) is the point on the I-V curve at which the PV module works with maximum power output.
- The short-circuit current (Isc) is the maximum current output of a module.
- The open-circuit voltage (Voc) is the maximum output voltage of a module.
Since PV modules in the field are not working under STC, the actual performance could be ten to fifteen percent lower than that of the STC rating.

Above: I-V characteristics of a PV module at various irradiance, constant temperature
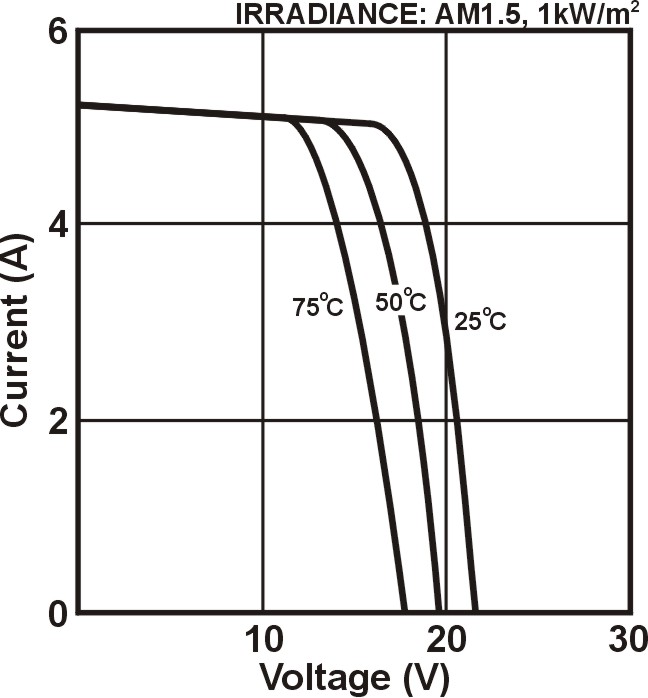
Above: I-V characteristics of a PV module at various temperature, constant irradiance