Grid Connection
Introduction
Renewable energy (RE) power generation systems (e.g. solar energy generation systems, wind turbines, biogas power generation systems) are usually built at locations close to the end users to fulfill their own electricity needs, or supplement part of their electricity needs. RE power generation systems can be designed either as standalone systems or grid-connected systems.
The utility grid is a power delivery network made of substations and cables and overhead lines, for the transmission and distribution of electricity from the power stations to the users throughout a service area.
RE power generation systems connected to the utility grid can be considered as "distributed generation sources", because they usually connect to the utility grid at the distribution voltage levels.
In Hong Kong, there are two power companies, each operating its own grid. The Hongkong Electric Company Limited (HKE) supplies electricity to users on Hong Kong Island and some outlying islands. The CLP Power Hong Kong Limited (CLP) supplies electricity to users in Kowloon, the New Territories, Lantau Island, and some outlying islands. In Hong Kong, the main power transmission voltage levels are 400kV (CLP) or 275kV (HKE), and 132kV, while the main distribution voltage levels are 11kV and 380V.
Direct and indirect grid-connection
Depending on the mode of interaction with the utility grid, grid-connected RE power generation systems can divided into two major types - the direct grid-connection type and the indirect grid-connection type.

Direct grid connection
For direct grid-connection type, the RE power generation system feeds its output directly into the utility grid.
For conventional wind turbines, induction generators are used which generate electricity at mains frequency. The induction generator is coupled with the utility grid through a step-up transformer. For biogas power generation systems, synchronous generators are used which also generate electricity at mains frequency.
For solar energy generation systems, the outputs of the solar photovoltaic (PV) arrays are DC. Inverters are needed to convert DC electricity into AC electricity.
The power output of a directly grid-connected RE power generation system is consumed by electricity users connected to the grid in the vicinity of the RE system.
Indirect grid connection
For indirect grid connection type, the output of the RE power generation system is fed into the electrical distribution system of the site. Both the utility grid and the RE power generation system supply electricity to the site at the same time.
An indirectly grid-connected RE power generation system is normally constructed by the electricity user, and its power output is consumed mainly within the site. Very often, the output of an indirectly grid-connected RE power generation system can only meet a small portion of the electricity needs of the site.
Benefits of grid-connection for user-constructed RE power generation systems
For an user-constructed RE power generation systems, it can be designed either as a standalone (off-grid) system, or an indirectly grid-connected system.
For a standalone system, storage batteries are often required, in particular for RE types which are intermittent in nature, such as solar energy or wind energy.
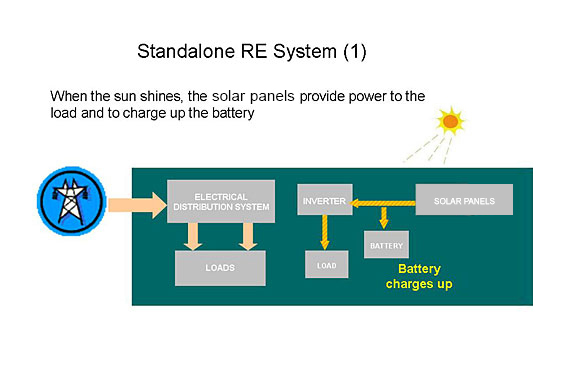

For a grid-connected system which is connected to the electrical distribution system of the site, the power flow from the utility grid will compensate for the fluctuation in the power output of the RE power generation system.

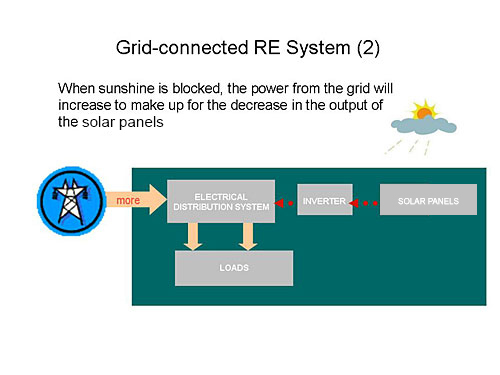
In summary, the benefits of grid connection for user-constructed RE power generation system are:
(a) Lower cost - Standalone (off-grid) systems are usually oversized to ensure continuity of electricity supply to the loads at all times. Therefore under some conditions, the output of the system cannot be fully utilized. Furthermore, the storage batteries require additional investment, building space, and routine maintenance. There will also be energy losses in the charging-discharging process. On the other hand, the output of a grid-connected system can always be fully absorbed by the loads (given that the output is often only able to meet a small portion of the total electricity demand of the site), and storage batteries are not required.
(b) Better reliability of supply - In the case of a standalone system, the power supply to the loads connected to the system will be lost if there are any faults in the system. On the other hand, for a grid-connected system, the utility grid will always make up for the loss of power output from the RE system. Sometimes, the user will not even notice that there is a problem in the RE system, until the time of routine maintenance.
A set of technical guidelines have been produced for indirect grid-connection of user-constructed RE power generation systems. More information is given in the Grid Connection - Technical Guidelines section.
Anti-islanding function
For grid-connected RE power generation systems, anti-islanding function is required to disconnect the RE system in case the part of the grid in the vicinity of the RE system experiences a loss of main power sources.
In the case of a directly grid-connected RE system, the main purpose of anti-islanding function is to prevent the situation where the RE power generation system continues to provide power supply to that part of the grid isolated from the main power sources, thus forming an "island" isolated from the rest of the grid.
In the case of an indirectly grid-connected RE system, the main purpose of anti-islanding function is to prevent the situation where the RE system continues to provide power supply to the loads at the site, when the grid supply to the site is lost. It also prevents back-energization of the grid from the RE power generation system. Furthermore, the anti-islanding function is often required to react quickly to avoid interfering with the auto-switching or auto-reclosing actions on the side of the grid under fault conditions.
Examples of grid-connected systems
The 800 kW wind turbine on Lamma Island built by The Hongkong Electric Company Limited is a well-known example of a directly grid-connected RE power generation system in Hong Kong.
The indirectly grid-connected 350kW solar energy generation system at EMSD Headquarters, put into service in 2005 as a demonstration project.
Refer to Example Projects section for details.